Although there are enough resources on the web about Git, I will keep this one for my own reference. Minimal Git version required 1.7.2.
TOC
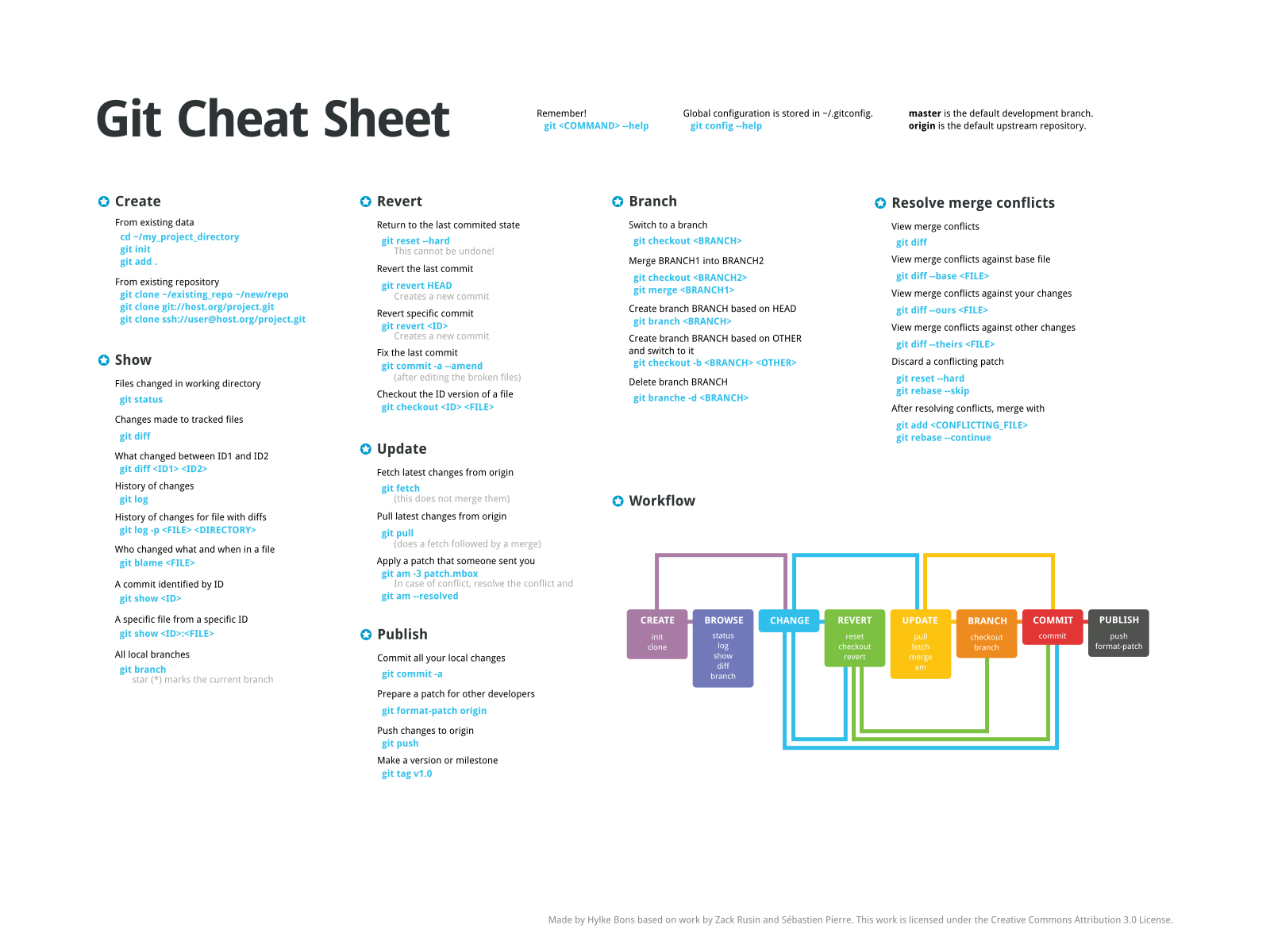
Git cheat sheet saves you from learning all the commands by heart. Be free to contribute, update the grammar mistakes. You are also free to add your language file. Git Cheat Sheet English. Git Cheat Sheet. Commands Getting Started. Configuration git config -global color.ui true git config -global push.default current git config -global core.editor vim git config -global user.name 'John Doe' git config -global user.email foo@citrix.com git config. By watching this video you will be able to understand the basic git commands with examples. Please comment here, in case of any query. Git cheat sheet for network nuts students. Contribute to kehbixgit/git-cheat-sheet development by creating an account on GitHub.
Legend
- index: staging area (Imagine you are loading sand into the truck with bucket. Well, the bucket is like index and truck like a repository :)
- <sha1>: sha1 hash of commit
- <file>: path to the file (path/to/file.ext)
- <branch>: branch name
- <repository>: remote repository name
Info
Search the history for a change matching a pattern
Useful options:
Find commits where files were deleted
Checkout deleted file in the working tree
Checkout a file from another branch into the working tree
Only show the content of a file from a specific revision
Show diff between branches detecting renames
Show file's history
Show changes on a branch that is not merged upstream
Show log with changed files
Get latest tag in the current branch
Find out if a change is part of a release
Find out which branch contains a change
Adding
Add changes to the index chunk by chunk
- y: stage this chunk
- n: do not stage this chunk
- s: split this chunk into smaller chunks
- e: edit this chunk
Branching
Create local branch
If not provided, Git uses HEAD as the new branch start point.
or
Delete local branch
Delete already merged branch
Force branch deletion
Patching
Copy commit range from one branch to another
Pick from start <sha1> commit till end <sha1> commit.
Creating and applying patches
By default Git will create a patch for every commit. Use --stdout > <patch>.patch for combined patch.
Create patches for the last N commits (each commit in it's own patch).
Create patches containing all commits from the current branch against another <branch> branch (each commit in it's own patch).
Using Github For Documentation
Creating combined patch.
Check what changes are in the patch
Test the patch before applying Teltonika port devices driver download for windows.
Apply patch
Undoing
git reset contains great explanation and examples.
Split commit
--soft option will keep files in the index.
Undo a merge or pull
Undo a merge or pull inside a dirty work tree
Revert a bad commit
Checkout a deleted file into the work tree
Remotes
Crete a new local branch by pulling a remote branch
Track a remote branch with an existing local
Delete remote branch
Prune remote-tracking branches that are deleted from a remote repo
Change remote URL
Subtree
--squashdo not preserve history (squash history)
Add subtree as non-remote repository
Add subtree
Pull subtree
Add subtree as remote repository
Add remote
Add subtree
Pull subtree changes
Push subtree changes
Submodules
Update submodules
Update submodule's URL
Edit the .gitmodules file, then run:
Remove submodule
- remove the submodule's entry in the .gitmodules file
- remove the submodule's entry in the .git/config
- run
git rm –cached path/to/module- without a trailing slash! - remove the submodule from the filesystem, run
rm -rf path/to/module/ - commit changes
Additional resources
Create repositories
A new repository can either be created locally, or an existing repository can be cloned. When a repository was initialized locally, you have to push it to GitHub afterwards.
$ git init
The git init command turns an existing directory into a new Git repository inside the folder you are running this command. After using the git init command, link the local repository to an empty GitHub repository using the following command:
$ git remote add origin [url]
Specifies the remote repository for your local repository. The url points to a repository on GitHub.
$ git clone [url]
Clone (download) a repository that already exists on GitHub, including all of the files, branches, and commits
The .gitignore file
Sometimes it may be a good idea to exclude files from being tracked with Git. This is typically done in a special file named .gitignore. You can find helpful templates for .gitignore files at github.com/github/gitignore.
Synchronize changes
Synchronize your local repository with the remote repository on GitHub.com
$ git fetch
Downloads all history from the remote tracking branches
$ git merge
Github Search Cheat Sheet
Combines remote tracking branches into current local branch
$ git push
Uploads all local branch commits to GitHub
$ git pull
Updates your current local working branch with all new commits from the corresponding remote branch on GitHub. git pull is a combination of git fetch and git merge
